Sensitivity (electronics)
The sensitivity of an electronic device, such as a communications system receiver, or detection device, such as a PIN diode, is the minimum magnitude of input signal required to produce a specified output signal having a specified signal-to-noise ratio, or other specified criteria.
Sensitivity is sometimes improperly used as a synonym for responsivity.
- Microphones
- The sensitivity of a microphone is usually expressed as the sound field strength in decibels (dB) relative to 1 V/Pa (Pa = N/m2) or as the transfer factor in millivolts per pascal (mV/Pa) into an open circuit or into a 1 kilohm load.
- Loudspeakers
- The sensitivity of a loudspeaker is usually expressed as dB / 2.83 VRMS at 1 metre. This is not the same as the electrical efficiency; see Efficiency vs Sensitivity.
- Hydrophones
- The sensitivity of a hydrophone is usually expressed as dB re 1 V/µPa.
Sensitivity in a receiver is normally defined as the minimum input signal 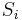 required to produce a specified signal-to-noise S/N ratio at the output port of the receiver and is defined as the mean noise power at the input port of the receiver times the minimum required signal-to-noise ratio at the output of the receiver:
required to produce a specified signal-to-noise S/N ratio at the output port of the receiver and is defined as the mean noise power at the input port of the receiver times the minimum required signal-to-noise ratio at the output of the receiver:
where
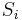 = sensitivity [W]
= sensitivity [W]- k = Boltzmann's constant
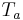 = equivalent noise temperature in [K] of the source (e.g. antenna) at the input of the receiver
= equivalent noise temperature in [K] of the source (e.g. antenna) at the input of the receiver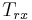 = equivalent noise temperature in [K] of the receiver referred to the input of the receiver
= equivalent noise temperature in [K] of the receiver referred to the input of the receiver- B = bandwidth [Hz]
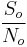 = Required SNR at output [-]
= Required SNR at output [-]
Because receive sensitivity indicates how faint an input signal can be to be successfully received by the receiver, the lower power level, the better. Lower power for a given S/N ratio means better sensitivity since the receiver's contribution is smaller. When the power is expressed in dBm the larger the absolute value of the negative number, the better the receive sensitivity. For example, a receiver sensitivity of -98 dBm is better than a receive sensitivity of -95 dBm by 3 dB, or a factor of two. In other words, at a specified data rate, a receiver with a -98 dBm sensitivity can hear signals that are half the power of those heard by a receiver with a -95 dBm receiver sensitivity.
References
This article incorporates public domain material from the General Services Administration document "Federal Standard 1037C" (in support of MIL-STD-188).